Scaled Scores
Most psychological tests base performance off of scaled scores and standard scores. Often, scaled scores are reported if the psychological test that was used was longer and had several sub-tests within it. A scaled score typically tells us how well a child did on a specific sub-test, and a standard score typically tells us how well a child did on a broad domain (which is often made of sub-tests).
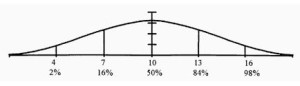
Scaled Scores have a score range of 0 – 19 points, with an average score of 10 points. These scores are typically used for “Sub-tests,” which are smaller components of a larger psychological test, such as the WISC-V, the NEPSY-2, or the DKEFs.
Scaled scores have a standard deviation (a term briefly introduced above) of 3 points. What does this mean? Simply put, most children of the same age will score between a 7 and 13, and thus fall within the low average (7) to high average range (13). It is statistically typical for a child to perform within one standard deviation (3 points) of the average score, in either direction. An important cautionary statement is that “average” is a broad term and parents should take note of where their child falls within the average range. Most psychologists will agree that a child who scores a 7 (low average) has significantly different performance than a child who scores a 13 (high average). Whereas, three children who score a 9, 10, and 11 are likely more comparable in their “average” performances.
If a child were to score more than one standard deviation below, or above the mean: a greater difference of 3 points (either less than a 7, or more than a 13), such a deviation from the mean indicates uniquely high or uniquely low performance. A child who scores more than one standard deviation BELOW the mean (scoring a 5, for example) will have a very low percentile rank. This means that their score was better than only a small number of peers in the norm group; most of the norm group performed better than them. A child who scores more than one standard deviation ABOVE the mean (scoring a 16, for example) will have a very high percentile rank. This means that their score was better than most of their peers in the norm group; the child performed better than most of the norm group.
Visit the South County Child & Family Consultants website for more great articles!
Receive online class information and helpful tips from Dr. Randy Kulman's LearningWorks for Kids |